Galaxy Docker instance¶
The Laniakea Galaxy Docker application run a Galaxy Docker container inside a Centos 7 virtual machine. The Official Galaxy Docker image is used. Currently, Laniakea supports the following Docker images:
- bgruening/galaxy-stable
- laniakeacloud/galaxy-covacs
- laniakeacloud/galaxy-gdc_somatic_variant
- bgruening/galaxy-rna-workbench
- laniakeacloud/galaxy-epigen
Note
Docker is configured to install all docker-engine files on /export, i.e. in the external storage.
Configuration files¶
The Docker configuration is slighty customized to make the Galaxy experience as similar as possible to the one on the virtual machine.
/etc/galaxy/.myenv.sh: file with the environment variables of the Docker container.The customized variables are:
GALAXY_CONFIG_TOOL_DATA_TABLE_CONFIG_PATH: tool_data_table_conf.xml specific for the galaxy flavour (see section Galaxy Flavours)GALAXY_CONFIG_ADMIN_USERS: admin_user - the email selected in the laniakea dashboardGALAXY_CONFIG_BRAND: Galaxy brand - the Instance description inserted in the laniakea dashboardGALAXY_CONFIG_REQUIRE_LOGIN: true - avoid anonymous login.GALAXY_CONFIG_ALLOW_USER_CREATION: true - allow user creation.GALAXY_CONFIG_ALLOW_USER_IMPERSONATION: false - allow user impersonation.GALAXY_CONFIG_NEW_USER_DATASET_ACCESS_ROLE_DEFAULT_PRIVATE: true - By default, users’ data will be public, but setting this to True will cause it to be private.GALAXY_CONDA_PREFIX: path to _conda prefixGALAXY_CONFIG_CONDA_AUTO_INIT: true - conda auto-startGALAXY_CONFIG_CONDA_AUTO_INSTALL: true - conda auto-install/etc/galaxy/tool_data_tables: directory with the tool_data_table_conf.xml files. A detailed description of Laniakea Galaxy flavours configuration for the reference data is here: Galaxy Flavours.
CVMFS configuration¶
The CVMFS repository selected in the Lanikaea dashboard is automatically configured and mounted inside the docker directory /cvmfs. The corresponding configuration files are in the directory /etc/cvmfs.
Galaxy docker usage¶
Galaxy docker logs¶
SSH login in the virtual machine and type:
$ sudo docker logs --tail 200 -f galaxydocker
Enter in the Docker¶
In order to access to the Galaxy container, SSH login in the virtual machine and execute the following command:
$ sudo docker exec -it galaxydocker bash
Main directories in the Docker¶
Main Galaxy directories inside the Docker container are in /export:
- ftp:
/export/ftp - database:
/export/database - conda:
/export/tool_deps/_conda
Check Galaxy configuration¶
In order to see the Galaxy Docker configuration, SSH login in the virtual machine and execute the following command:
$ sudo docker exec -it galaxydocker echo $GALAXY_CONFIG
Data upload: FTP¶
Of course, the Galaxy Docker container allows user to upload data through FTP.
The procedure is similar to that described in the Proftpd section here: /user_documentation/galaxy_production_environment/galaxy_production_environment_configuration.rst.
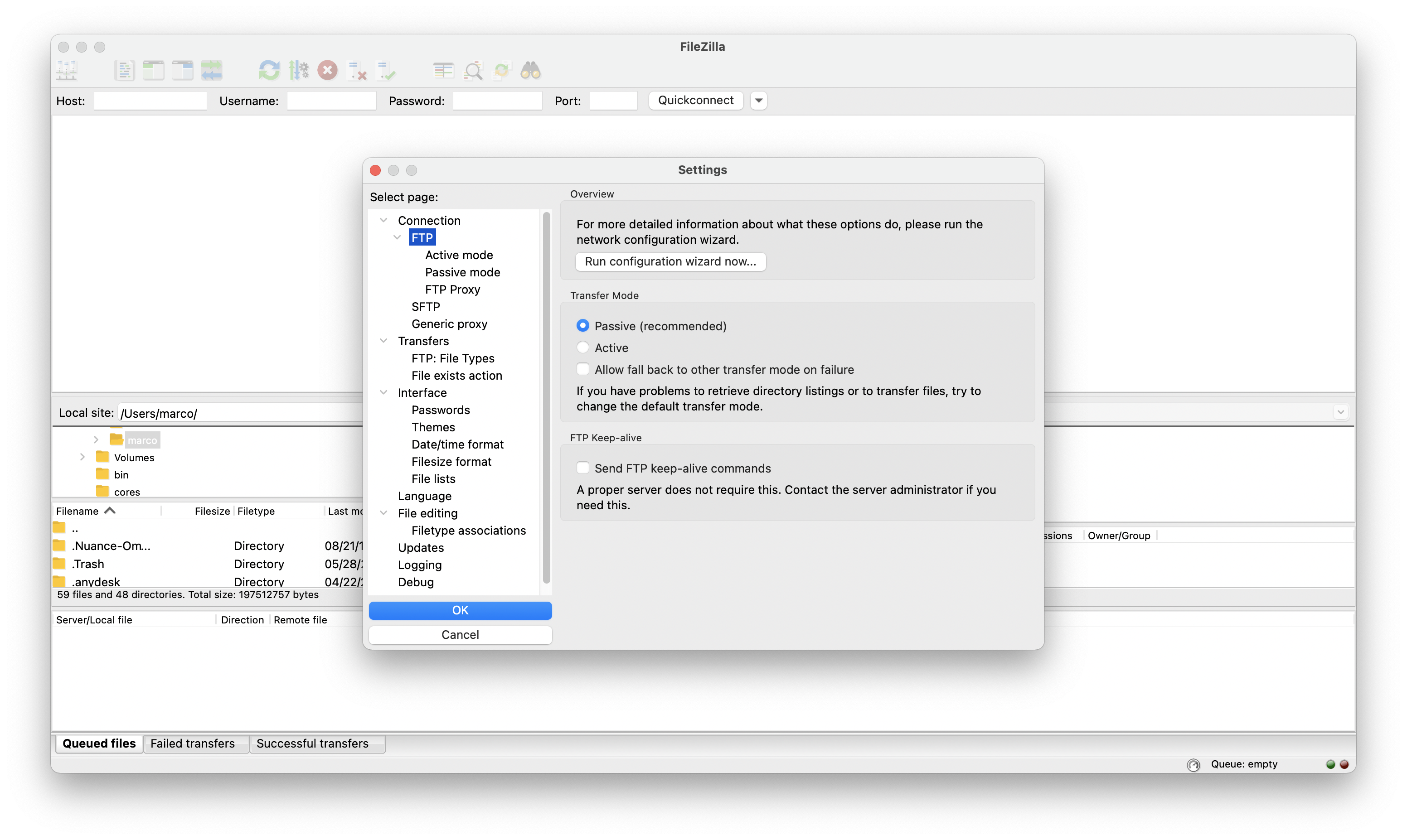
Moreover, you need to enable FTP Passive mode. Go to Settings..., then to FTP and flag Passive (recommended), as shown in the following picture.
For those using the command line tool, you can enable/disable the passive mode by typing passive. First connect to the server then type:
passive
and you will be in passive mode.